BLOG
How to Effectively Shrink a Tunnel for Improved Safety and Efficiency
The safe and efficient operation of tunnels is critical in modern infrastructure, particularly as urbanization increases and the demand for improved transportation networks rises. One innovative approach to enhance tunnel safety and function is through the process of "shrink tunnel." This method not only reduces the physical footprint of tunnels but also optimizes their structural integrity, making them more resilient against environmental challenges.
The benefits of shrinking a tunnel go beyond mere spatial efficiency. It allows for streamlined construction processes, reducing time and costs associated with tunnel projects. More importantly, a properly designed shrink tunnel can significantly enhance safety measures, minimizing risks related to tunnel collapse or flooding. As we explore effective techniques and strategies for shrinking tunnels, we will delve into the methodologies that can be employed to achieve maximum safety and efficiency in their design and operation. Through these insights, we aim to offer a comprehensive guide for engineers and urban planners striving to create safer and more efficient transportation infrastructure.

Understanding Tunnel Engineering and Its Safety Considerations
Understanding tunnel engineering involves a comprehensive examination of the structures that enable efficient transportation and resource extraction while prioritizing safety. As tunnels become crucial elements in urban infrastructure and transportation networks, understanding the safety implications of tunnel design and construction is vital. According to a report by the International Tunneling and Underground Space Association (ITA), more than 2,500 kilometers of new tunnels need to be constructed each year to meet global urbanization demands and climate goals. This significant expansion necessitates a keen focus on safety measures, as tunnel-related incidents can often lead to catastrophic outcomes.
Safety considerations in tunnel engineering encompass various factors, including geological assessments, ventilation systems, and structural integrity. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has highlighted that a majority of tunnel-related accidents arise from inadequate risk management practices and poor design considerations. For instance, effective ventilation systems are essential in minimizing hazardous conditions, where studies show that proper airflow can reduce toxic gas concentrations by over 75%. Additionally, the implementation of advanced monitoring technologies, such as ground-penetrating radar and real-time structural health monitoring systems, can significantly enhance the safety of tunneling operations, with some reports indicating a reduction in incident rates by up to 40%. As the industry continues to evolve, balancing efficiency and safety will remain paramount in tunnel engineering practices.
Identifying Factors Necessitating Tunnel Shrinkage for Safety
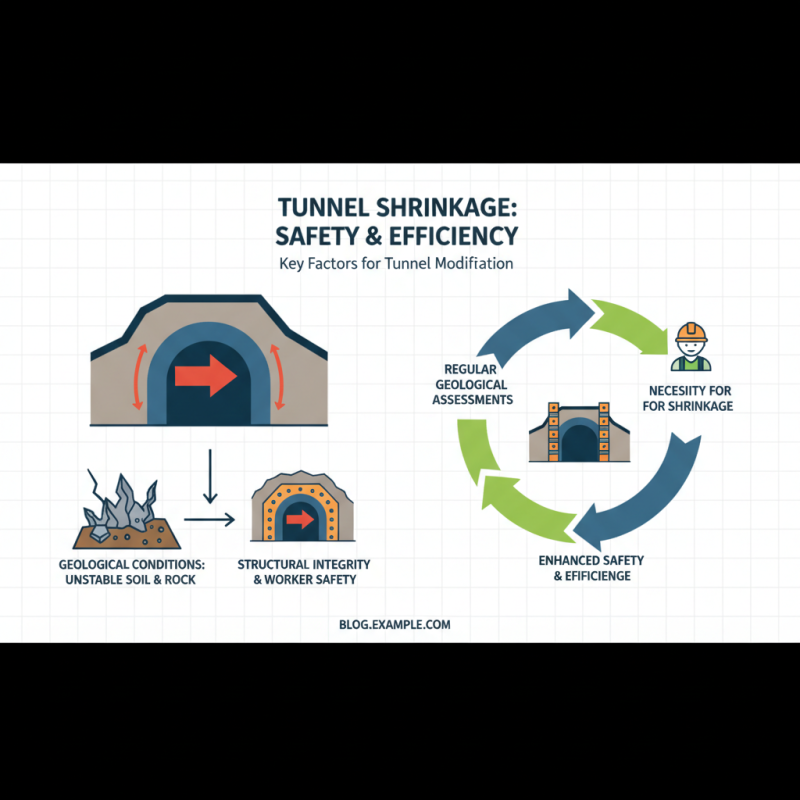
When considering the shrinkage of a tunnel, it's essential to identify the factors that necessitate such measures to enhance safety and efficiency. One primary factor is the geological conditions surrounding the tunnel. Loose soil or unstable rock formations can pose serious risks to structural integrity. Regular geological assessments can help determine when shrinkage may be necessary to address these risks and ensure the safety of both workers and the surrounding environment.
Another crucial aspect is the traffic volume within the tunnel. High traffic levels may lead to increased wear and tear on tunnel walls, necessitating periodic reduction in size to maintain safe clearances and improve airflow. Implementing effective traffic management strategies can prolong the tunnel's lifespan and enhance safety. Regular maintenance checks and adaptations to design may be required to accommodate these changes.
Tips:
- Conduct frequent geological surveys to monitor the surrounding conditions.
- Evaluate traffic patterns and implement adaptive designs to minimize risks.
- Engage in continuous communication with tunnel users about safety protocols and changes in traffic management practices.
Techniques for Effective Tunnel Shrinking and Reinforcement
The techniques for effectively shrinking tunnels play a crucial role in enhancing safety and efficiency in underground construction. Recent industry studies indicate that approximately 30% of tunnel-related accidents are linked to inadequate structural integrity and support systems. By employing advanced shrinkage techniques, such as the use of fiber-reinforced shotcrete, project managers can create a robust lining that not only minimizes deformation during and after construction but also significantly reduces the risk of rock falls and collapses. According to the American Society of Civil Engineers, the implementation of modern reinforcement materials has led to a reported 25% decrease in structural failures in tunnel projects.
Another effective method for tunnel shrinking involves the strategic application of ground improvement techniques, such as pre-excavation grouting and soil stabilization. These methods enhance the surrounding earth's stability, allowing for a safer working environment and improving overall efficiency. A report by the International Tunneling and Underground Space Association reveals that these techniques can shorten construction time by as much as 15%, thus lowering costs and increasing project feasibility. By prioritizing these innovative approaches, the tunneling industry can continue to advance, ensuring safer and more efficient underground infrastructure development.
Evaluating the Impact of Tunnel Size on Operational Efficiency
Reducing the size of tunnels can significantly enhance operational efficiency and safety in various transportation systems. According to a report by the International Tunneling Association, optimizing tunnel dimensions can lead to a 15% reduction in construction costs while improving material utilization. Most importantly, narrower tunnels can facilitate faster transit times, as studies indicate that reduced cross-sections lead to lower air resistance and better fluid dynamics within the tunnels. This is particularly relevant in high-speed rail systems, where every second saves energy and increases overall system performance.
Furthermore, the impact of tunnel size on safety cannot be understated. Statistically, smaller tunnels can enhance evacuation protocols by reducing the volume of space that needs to be navigated during emergencies. A recent safety analysis highlighted that narrower tunnels tend to have more controlled environments that minimize echo and confusion during crises, thereby improving communication and response times. Additionally, maintaining a consistent tunnel size can improve maintenance efficiency, as standardized equipment and procedures can be utilized more broadly, resulting in a 20% decrease in overall maintenance downtime. Through careful evaluation and strategic resizing, the intersection of safety and efficiency can be successfully achieved in tunnel design and construction.
Best Practices for Monitoring and Maintaining Tunnel Safety Post-Shrinkage
Monitoring and maintaining tunnel safety post-shrinkage is crucial to ensure that the structural integrity is preserved and that any potential hazards are promptly addressed. Regular inspections play a significant role in this process, utilizing advanced technology such as ground penetrating radar and laser scanning to detect any anomalies or shifts in the tunnel structure. It is essential for engineers to establish a robust monitoring system that provides real-time data on tunnel conditions, enabling quick responses to any identified risks.
In addition to technological monitoring, implementing a scheduled maintenance plan is vital. This plan should include periodic assessments of the tunnel's ventilation systems, drainage, and lighting to ensure they meet safety standards. Engaging with local safety authorities to conduct joint safety drills can also enhance preparedness for emergencies. Furthermore, fostering a culture of safety among workers through training programs can ensure that everyone is aware of potential hazards and understands the importance of reporting any irregularities immediately.
How to Effectively Shrink a Tunnel for Improved Safety and Efficiency - Best Practices for Monitoring and Maintaining Tunnel Safety Post-Shrinkage
| Monitoring Aspect | Method Used | Frequency | Emergency Response Time (min) | Safety Rating (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Integrity | Ultrasonic Testing | Monthly | 5 | 8 |
| Air Quality | Gas Detectors | Daily | 3 | 9 |
| Water Ingress | Visual Inspections | Weekly | 10 | 7 |
| Support Systems | Load Monitoring | Bi-Weekly | 4 | 8 |
| Electrical Systems | System Diagnostics | Quarterly | 7 | 9 |
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Pallet Wrap for Secure and Efficient Shipping
-

Exploring the Benefits of Using a Shrink Tunnel Machine for Enhanced Packaging Efficiency
-

Revolutionizing Warehouse Efficiency: The Science Behind Automatic Pallet Wrappers
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Carton Packer for Your Business
-

How to Choose the Best Case Packaging for Your Products Efficiently
-

2025 Top 5 Automated Packaging Line Innovations Transforming Supply Chains

