BLOG
What is an Automated Guided Vehicle and How Does it Work?
The rise of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) is reshaping industries worldwide. According to a recent industry report, the AGV market is expected to grow by over 14% annually until 2027. These vehicles enable efficient transportation of materials in warehouses and factories. The technology relies on sensors, cameras, and sophisticated algorithms to navigate their surroundings.
AGVs are not just about speed. They enhance accuracy too. They reduce human error and improve safety. However, challenges remain. Some companies still struggle with AGV integration into existing systems. Their dependency on stable infrastructure can lead to limitations. Unexpected obstacles can also disrupt their operational flow.
Despite these hurdles, the potential of AGVs is undeniable. They offer significant savings in labor costs and improve overall productivity. As industries continue to adopt this technology, understanding how automated guided vehicles work becomes crucial for maximizing their benefits. The future looks bright, but reflection on current challenges is necessary for further advancements.

Definition and Overview of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles, or AGVs, are innovative machines that transport goods within a facility. They are equipped with various sensors, cameras, and software to navigate through their environment. Typically, AGVs follow marked paths or wires on the ground. This system allows for precise movement and efficient operation. However, the technology is still evolving.
AGVs can handle repetitive tasks and reduce the risk of manual errors. They can transport items between different workstations and warehouses. This capability increases productivity, but it is not without flaws. Sometimes, they struggle with complex environments. Changes in layout can pose significant challenges. They also require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
The integration of AGVs into businesses has not been universally easy. Operators still need to train to manage these vehicles effectively. There are instances where humans and AGVs might miscommunicate during operations. It raises questions about efficiency and safety. There is still room for improvement and development in this field, making it an exciting area for future research.
Overview of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) Usage in Different Industries
This bar chart illustrates the number of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) deployed across different industries. Manufacturing leads with the highest deployment, reflecting its crucial role in production efficiency. Warehousing and healthcare also show significant usage, highlighting the versatility of AGVs in various sectors.
Key Components and Technologies Utilized in AGVs
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are transforming logistics and manufacturing. These vehicles rely on specific components and technologies to navigate and perform tasks. Key parts include sensors, control systems, and navigation methods. Sensors help AGVs detect their environment. Popular options are laser scanners and cameras. They allow AGVs to avoid obstacles effectively.
Tips: When selecting AGV components, consider your specific needs. Evaluate your work environment. Ensure sensors are compatible with your operations. Keep in mind that not all navigation methods work equally well in every setting. Regular maintenance is essential to keep AGVs running smoothly. Small issues can lead to bigger problems if neglected.
Working Mechanisms: Navigation and Control Systems of AGVs
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are advanced systems that perform tasks with minimal human intervention. Their successful operation relies heavily on two core mechanisms: navigation and control systems.
Navigation methods can vary widely. Some AGVs use magnetic strips, while others rely on lidar or vision systems. This flexibility allows adaptability in various environments. However, each method has its limitations. For example, magnetic navigation can struggle in dynamic settings.
Control systems direct AGVs to their destinations. They can be programmed with predefined routes or operate in real time. Real-time systems respond to changes in their environment, improving efficiency. Yet, this responsiveness can also create challenges. Unforeseen obstacles may confuse the vehicle, leading to delays or errors. These situations reveal the need for continuous improvement in AGV technology.
Tips: Regularly test AGV systems in your environment. Identify any weaknesses. Ensure drivers and operators understand potential issues. Training is vital for optimal performance. Keep monitoring technology developments. This helps in understanding new navigation and control methods. Embracing innovation can lead to enhanced productivity.
Applications of AGVs in Various Industries and their Impact
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have become vital tools across various industries. In manufacturing, they transport raw materials and finished goods. These vehicles reduce manual labor and enhance efficiency. They navigate using sensors and predefined paths, yet challenges remain. Adapting to real-time changes in their environment is still a hurdle.
In warehousing, AGVs streamline inventory management. They operate alongside human workers, minimizing accidents and bottlenecks. However, their integration requires careful planning. Each warehouse is unique, and one size does not fit all. The impact on productivity is significant, but optimization is often a continuous process.
Healthcare facilities also use AGVs for transporting medications and supplies. This reduces the burden on staff and improves patient care. Yet, the complexity of hospital layouts can complicate their operations. Some AGVs struggle in tight spaces or crowded areas. As industries explore new applications, ongoing improvements are essential to maximize their potential.
Future Trends and Innovations in Automated Guided Vehicle Technology
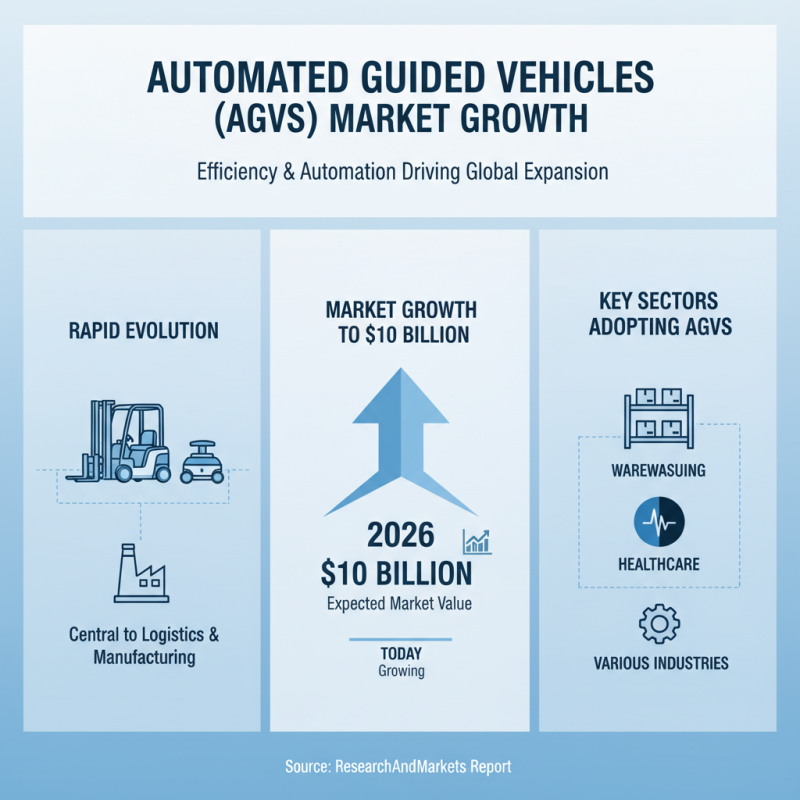
The world of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is evolving rapidly. As industries seek efficiency, AGVs are becoming central to logistics and manufacturing. A market research report from ResearchAndMarkets indicates that the AGV market is expected to grow to $10 billion by 2026. This growth reflects a shift toward automation in various sectors, including warehousing and healthcare.
Innovations in AGV technology are exciting but face challenges. Advanced sensors and artificial intelligence are enhancing navigation and safety. However, integration into existing systems remains complex. Many industries are still adapting to these tech changes. A report from Allied Market Research suggests that while 54% of businesses are investing in AGVs, 46% struggle with implementation. This gap shows the need for clearer strategies in adopting automated solutions.
Collaboration among technology developers, manufacturers, and end-users is crucial. This partnership can drive advancements in safety features and communication systems. Additionally, addressing workforce concerns about job displacement will be vital. A balance must be found between tech innovations and the human element in operations. AGVs hold great promise, but thoughtful implementation is necessary to maximize their benefits.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Trends in Automatic Packing Systems for Improved Efficiency
-

The Future of Food Safety Revolutionizing Automated Food Packaging Systems
-

How to Choose the Right Palletizer Machine for Your Warehouse Needs
-

Why You Need a Carton Erector for Streamlined Packaging Operations
-

Revolutionizing Efficiency in Manufacturing with an Automated Packaging Line for Sustainable Growth
-

Exploring the Benefits of Using a Shrink Tunnel Machine for Enhanced Packaging Efficiency

